KDDI announced that it has started deployment of TIP's DDBR as the internet gateway peering routers.
DDBR carrying live internet traffic will start helping KDDI to reduce the power consumption by about 46% and the rack space by about 40% compared to the traditional routers in KDDI production networks.
As 5G services expand use cases in mobile communications, 5G traffic is expected to increase rapidly due to the wide range and increase of connected terminals.
To sustain such growth, further system optimization such as lower power consumption, smaller size and lower cost systems would be required for the 5G network infrastructure.
Moreover, since the dedicated routers are needed to be deployed in each area of the carrier backbone networks, such as core, edge, and internet GW, the equipment capital cost increase as well as complexity of such operation has become a major issue.
To handle such issues, KDDI became a TIP participant to promote the development of open and disaggregated technologies for telecommunication systems. As a result, KDDI completed the DDBR technical requirements document in May 2021 and TIP announced the DDBR compliant vendors in March 2022. In March 2022 [Jump to the applicable section4], KDDI completed a final phase of commercial testing for DDBR.
KDDI's DDBR architecture has two key advantages:
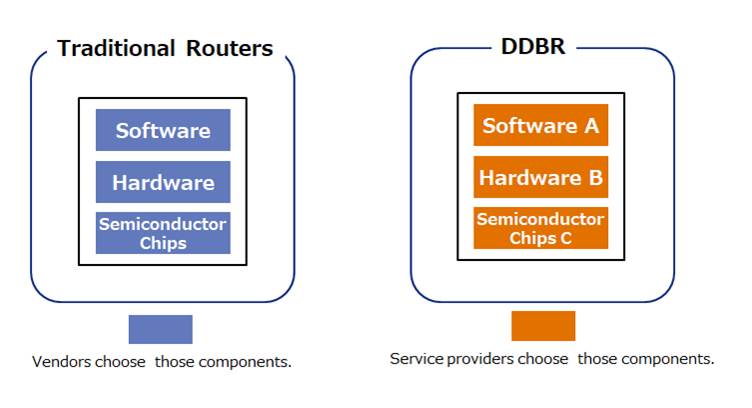
1. Optimal Merchant Silicon Selection and Configuration
Traditional routers comprise software, hardware and semiconductor chips chosen by one vendor. On the other hand, this DDBR comprises DriveNets Network Cloud software, hardware (40×100GE line card systems) from Delta Electronics, Inc. , and merchant silicon (Jericho2) from Broadcom, Inc. Only one Jericho2 inside the hardware box has enough capability to fulfill software/hardware features and scalability in KDDI production networks. As a result, DDBR leads to reduce the power consumption, the equipment capital cost and the rack space.
2. Sharing of Hardware Resource
In a carrier's traditional network architecture, the dedicated routers for core, edge and internet GW are deployed depending on each area. On the other hand, DDBR can utilize the same white box hardware infrastructure for multiple areas such as core, edge and internet GW. As a result, it will enable KDDI to share hardware spare parts in our backbone networks, leading to the reduction of the equipment capital cost.