At the recent at AWS re:Invent, AWS announced AWS Cloud WAN, a managed wide area network (WAN) service that makes it faster and easier for enterprises to build, manage, and monitor a unified global network that seamlessly connects cloud and on-premises environments.
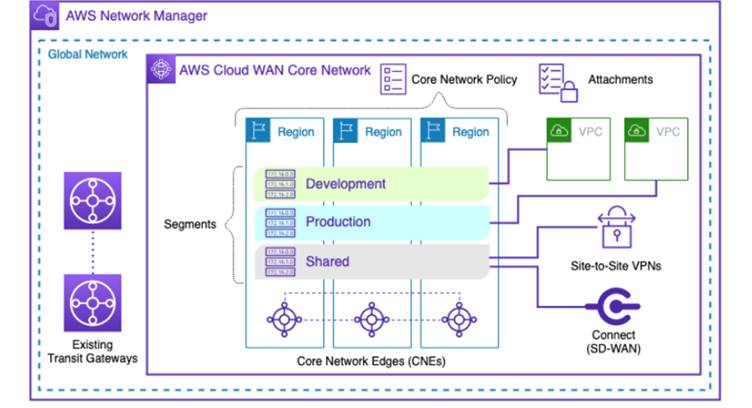
AWS Cloud WAN provides a central dashboard that enterprises can use to connect their on-premises branch offices, data centers, and Amazon Virtual Private Clouds (Amazon VPCs) across the AWS global network in just a few clicks. With AWS Cloud WAN, enterprises can get a complete view of their global network and use simple network policies to centrally configure and automate network management and security tasks. AWS Cloud WAN enables enterprises to use the AWS global network to provide a single unified network, which allows them to improve network health, performance, and security.
Many enterprises today run their operations across multiple environments, including on-premises data centers, branch offices, and AWS. To connect these environments together, customers build and manage their own global networks, while also leveraging networking, security, and internet services from multiple third-party providers. For connectivity between cloud environments, customers use AWS networking services like Amazon VPC to easily build a logically isolated virtual network on AWS, and AWS Transit Gateway to easily interconnect multiple VPCs. For connectivity between cloud and on-premises environments, customers use AWS Direct Connect to easily create a private connection between AWS and their data centers, or create a secure AWS virtual private network (VPN) connection. However, for connectivity between on-premises data centers and branch offices, customers must invest considerable time and money to build their own physical network or build a software-defined overlay network from third-party providers. All of these networks take a different approach to connectivity, security, monitoring, and managing performance, which results in an intricate patchwork of individual networks that is complicated to configure, secure, and manage. As a result of these burdens, networking teams struggle with managing an expanding mix of network technologies that are required to securely build, scale, and operate a global network.
AWS Cloud WAN is a managed WAN service that connects on-premises data centers, branch offices, and cloud resources to simplify operating a global network. With AWS Cloud WAN, enterprises can use a central dashboard and network policies to build, manage, and monitor a global network that spans multiple locations and networks—eliminating the need to configure and manage different networks individually using different technologies. Network teams can use simple network policies to specify the Amazon VPCs and on-premises locations they want to connect through AWS VPN, AWS Direct Connect, AWS Transit Gateway, and third-party software-defined WAN (SD-WAN) products, and AWS Cloud WAN generates a complete view of the network to monitor network health, security, and performance. Teams can also use network policies to automate routine network-management tasks like adding new sites or branch locations, isolating traffic between sensitive applications or locations, segmenting groups of networks to make it easier to manage network isolation between AWS and on-premises environments, or enabling specialized network or security services. For example, customers can increase their security posture by creating a policy that ensures that any network traffic from their branch locations must be routed through a network firewall before reaching their cloud resources. AWS Cloud WAN integrates with major SD-WAN and network appliance providers—including Aruba, Cisco Systems, Palo Alto Networks, and VMware—allowing customers to use and manage products and services from these providers. Enterprises can now use AWS Cloud WAN to simplify the way they build, manage, and monitor their networks with a central control plane.
To get started, customers connect their on-premises environments to AWS with the help of a telecommunications service provider. These connections bridge the gap between the customer’s data centers or colocation facilities and the AWS network, extending their existing WAN network to the cloud. Customers can then deploy a highly available global network by selecting the AWS Regions closest to their on-premises locations and then easily add or remove remote locations, data centers, or Amazon VPCs to and from their global network with just a few clicks in the AWS Cloud WAN console or using the AWS Cloud WAN application programming interface (API).
David Brown, Vice President of Amazon EC2 at AWS
With AWS Cloud WAN, customers can simplify how they manage a WAN by using a central dashboard to unify the multiple networks they manage today, implement network policies for performance and security, easily add locations, and automate advanced network settings. AWS Cloud WAN removes the difficulty of stitching together and managing multiple third-party tools so customers can now more easily keep their networks securely connected and high performing.