Today’s networking headlines are frequently grabbed by “5G” – the fifth generation of mobile technology. While it is true that 5G will go beyond 4G in terms of speeds and users that it will support, the true ambition of 5G is the vision of a new end-to-end system that provides a seamless and consistent user experience over a multitude of networks, devices, and user interactions. So, while many think of the mobile aspect of 5G, the reality is that underlying wired infrastructure will play a critical role in enabling the success of 5G.

John D’Ambrosia,
Chair,
Ethernet Alliance
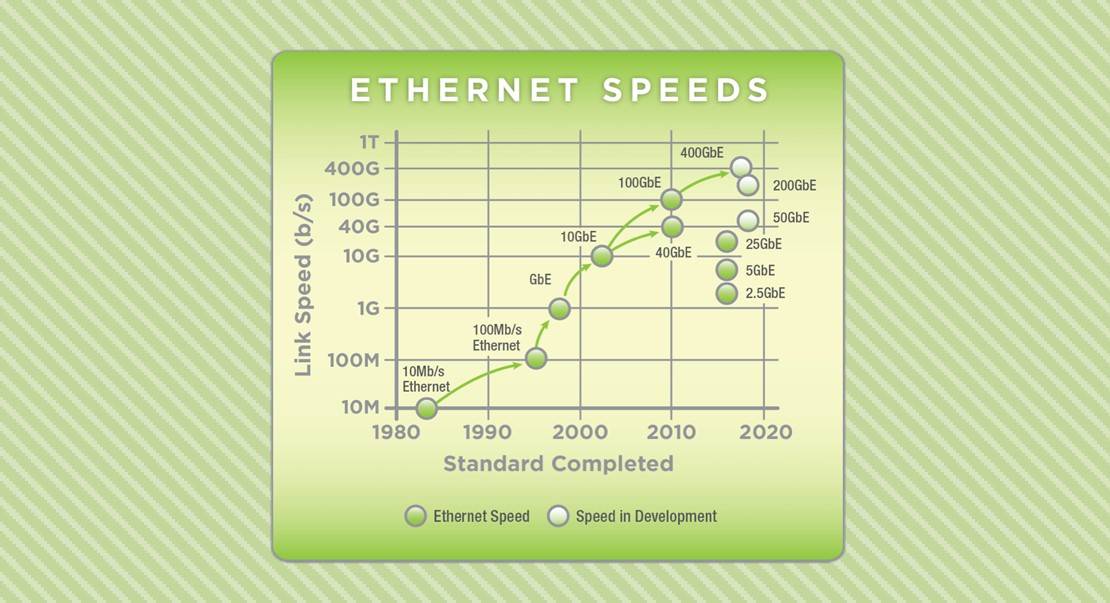
As the vision of 5G has been emerging over the past few years, Ethernet has been undergoing a metamorphosis, emerging from a technology that grew by factors of 10 to a technology that is delivering the solutions that different application spaces will need. And that is why the “Next Era of Ethernet” will play a foundational role in creating a fixed infrastructure to support the various demands of different 5G visions. From wireless backhaul networks, to enterprise networks, to data centers, Ethernet will provide a multitude of new solutions that will allow the scaling and delivery of even more bandwidth -
Higher bandwidth Ethernet single-mode fiber solutions ranging from 25 Gb/s to 400 Gb/s will be deployed throughout mobile networks providing “fat pipes” enabling metro reaches up to 40km.
Data centers will see a boost in their server interconnect infrastructure. Today’s typical deployment of top-of-rack switch configurations using a copper twin-axial cable server interconnect will be upgraded to 25GbE. Blade servers will leverage 25GbE backplane technology, as will end-of-row switch architectures using multi-mode fiber optics.
Enterprise mobility will be given a speed boost by the deployment of the IEEE 802.3bz-based 2.5GBASE-T and 5GBASE-T solutions that will provide wired access to the network for the massive amounts of data driven by the proliferation of wireless access points.
The Ethernet community is also targeting IoT and industrial applications requiring low Mb/s bandwidth solutions with new single pair copper based solutions that are currently in development within the IEEE 802.3 Ethernet Working Group.
In 2007 the Ethernet community decided to do both 40GbE and 100GbE. Ten years later, this decision continues to resonate, as the multitude of new solutions noted above, driven by the particular needs of their application space have emerged. This freedom, combined with the focus on delivering a truly new experience to the end-user is creating the truly dynamic environment of 2017. So while everyone is excited about not being tethered by a cable, the reality is that a multitude of Ethernet-enabled wired infrastructures will be deployed - laying the foundation for 5G and the next generation of mobility.
About The Author:
John D’Ambrosia is known in the industry for his efforts as Ethernet’s advocate. He is the Chairman of the Ethernet Alliance, an organization dedicated to the promotion of all Ethernet technologies. In his role as a Senior Principal Engineer at Huawei, John participates in several IEEE industry standards efforts that are driving Ethernet’s on-going evolution and its move to higher speeds. A popular blogger on Ethernet matters, Mr D’Ambrosia was awarded the IEEE-SA 2013 Standards Medallion and was inducted into the Light Reading Hall of Fame. His previous experience includes Dell, Force10 Networks, and Tyco Electronics.